Vietnamese air is an intricate blend of natural elements, climatic influences, and human activities that culminate in a unique atmospheric experience across the country. Understanding the unique characteristics of the air in Vietnam allows us to appreciate how it interacts with the environment, health, and cultural practices. This article delves into various aspects of Vietnamese air, examining its composition, climate zones, pollution, and much more.
1. Composition of the Atmosphere in Vietnam

The atmosphere above Vietnam is predominantly composed of standard gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and trace amounts of other gases including argon and water vapor. However, the unique characteristics of the Vietnamese air are greatly affected by local geographical features, urbanization, and seasonal changes.
1.1. Major Components of Vietnamese Air
The primary components of Vietnamese air mirror those found globally, with nitrogen making up about 78% and oxygen around 21%. Despite this similarity, localized variations exist due to environmental factors. The presence of moisture is one significant characteristic; the tropical regions of southern Vietnam often experience high humidity levels, contributing to a dense and warm atmosphere.
Moreover, industrialization has led to an increase in pollutants such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter. These pollutants are primarily released from vehicles, factories, and agricultural practices, altering the usual composition of the air.
1.2. Influence of Geography on Air Quality
The diverse topography of Vietnam significantly influences the characteristics of vietnamese air. Mountainous regions in the north often trap pollutants, leading to reduced air quality in certain areas. Coastal plains, on the other hand, benefit from sea breezes that help disperse contaminants, resulting in cleaner air. Urban centers like Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi face challenges due to concentrated emissions from transportation and industry. In contrast, rural areas generally experience better air quality due to lower population density and reduced industrial activity. Therefore, geography plays a crucial role in shaping the composition and quality of vietnamese air across the country.
1.3. Impact of Seasonal Changes
2. Climate Zones of Vietnam

The climate in Vietnam varies significantly from south to north, influencing the overall characteristics of the air. Understanding these climate zones provides insights into the environmental conditions that shape the atmosphere throughout the country.
2.1. Tropical Climate in the South
Southern Vietnam predominantly experiences a tropical climate characterized by high temperatures and substantial rainfall. This climate is essential for agricultural productivity, yet it presents specific challenges concerning Vietnamese air quality.
The high humidity levels combined with intense heat can create a stifling environment, especially in densely populated urban centers. Moreover, the region’s rapid economic development has led to increased vehicular traffic and industrial activities, exacerbating Vietnamese air pollution problems.
2.2. Temperate Climate in the North
Northern Vietnam exhibits a temperate climate with distinct seasonal changes, including hot summers and cold winters. The variation in temperature and humidity levels significantly affects the characteristics of Vietnamese air throughout the year.
During the winter months, air stagnation can occur, trapping pollutants close to the ground and creating smog conditions. This phenomenon highlights the need for targeted strategies to improve air quality during colder months, as respiratory problems can worsen among residents. This seasonal variation in Vietnamese air quality underscores the importance of implementing region-specific air quality management strategies.
2.3. Subtropical Influences in Central Vietnam
Central Vietnam enjoys a subtropical climate, characterized by a mix of both tropical and temperate conditions. The region often experiences typhoons and heavy rains, which can influence Vietnamese air quality by washing away pollutants.
However, the combination of agricultural practices and urbanization has resulted in localized air pollution issues. Thus, balancing the agricultural needs with sustainable practices is essential to ensure clean Vietnamese air for future generations.
3. The Role of Geography in Air Quality
3.1. Mountain Ranges and Their Effect on Weather Patterns
Mountain ranges, such as those found in northern Vietnam, have a profound impact on weather patterns and air quality. They can act as barriers, preventing the dispersal of air pollutants. As a result, low-lying areas may become trapped with unhealthy air, exacerbating pollution problems.
In addition to their effects on air movement, mountains can also influence precipitation patterns. Increased rainfall in mountainous regions can help mitigate pollution by cleansing the air, while drier periods may exacerbate air quality problems due to stagnant air.
3.2. Urban Areas vs. Rural Regions
The disparity in air quality between urban and rural areas of Vietnam sheds light on the influence of geography. Urban centers like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City suffer from high levels of pollution due to concentrated human activity, extensive transportation networks, and industrial facilities.
In contrast, rural regions often enjoy cleaner air with less exposure to pollutants. The open spaces, fewer automobiles, and agricultural practices contribute to a healthier atmosphere. However, rural areas are not exempt from pollution entirely, as agricultural burning and waste management practices can introduce contaminants into the air.
4. Pollution and Its Impact on Vietnamese Air

Pollution poses a significant threat to the quality of Vietnamese air, affecting the health and well-being of millions of people. Understanding the sources of pollution and the measures taken to combat it is crucial in addressing this ongoing challenge.
4.1. Major Sources of Air Pollution
Vietnam’s rapid economic development has led to increased pollution levels, with transportation, industrial emissions, and construction activities being the primary contributors.
Motor vehicles are one of the largest sources of air pollution in urban areas, emitting harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. The growing population and rising number of vehicles exacerbate the problem, leading to serious public health risks.
Industrial activities, particularly in manufacturing and processing sectors, contribute significantly to air pollution. Emissions from factories can release toxic substances, affecting both local air quality and overall environmental health.
4.2. Government Initiatives to Combat Pollution
Recognizing the alarming state of air quality, the Vietnamese government has undertaken initiatives aimed at addressing pollution concerns. Policies designed to regulate emissions from vehicles and industries have been implemented, along with efforts to promote cleaner technologies.
Public awareness campaigns focus on educating citizens about the importance of reducing pollution and adopting eco-friendly practices. Additionally, urban planning strategies aimed at developing green spaces and improving public transportation systems are integral to creating healthier living environments.
5. Natural Phenomena Affecting Air Quality

Natural events also contribute to fluctuations in air quality, with monsoons and dust storms having varying impacts on the Vietnamese atmosphere. Understanding these phenomena helps in preparing for and mitigating their effects.
5.1. Monsoons and Their Effects
Monsoons play a crucial role in shaping Vietnam’s climate, bringing substantial rainfall during the wet season. This influx of moisture significantly influences air quality by washing away pollutants and refreshing the atmosphere.
However, the arrival of monsoons can also bring challenges. Heavy rains may lead to flooding, which can wash pollutants into water sources and adversely affect local ecosystems. Moreover, the aftermath of monsoons may leave behind residual air quality issues that require attention.
5.2. Dust Storms and Their Consequences
Dust storms, while less frequent, can pose significant threats to air quality in Vietnam. These storms can transport large quantities of dust and particulate matter, reducing visibility and worsening respiratory conditions.
In particular, the northern regions, with their unique geographical formations, may occasionally experience dust storms influenced by desert winds. These episodes highlight the vulnerability of Vietnam’s air to natural phenomena, necessitating proactive measures to safeguard public health.
6. Health Implications of Air Quality
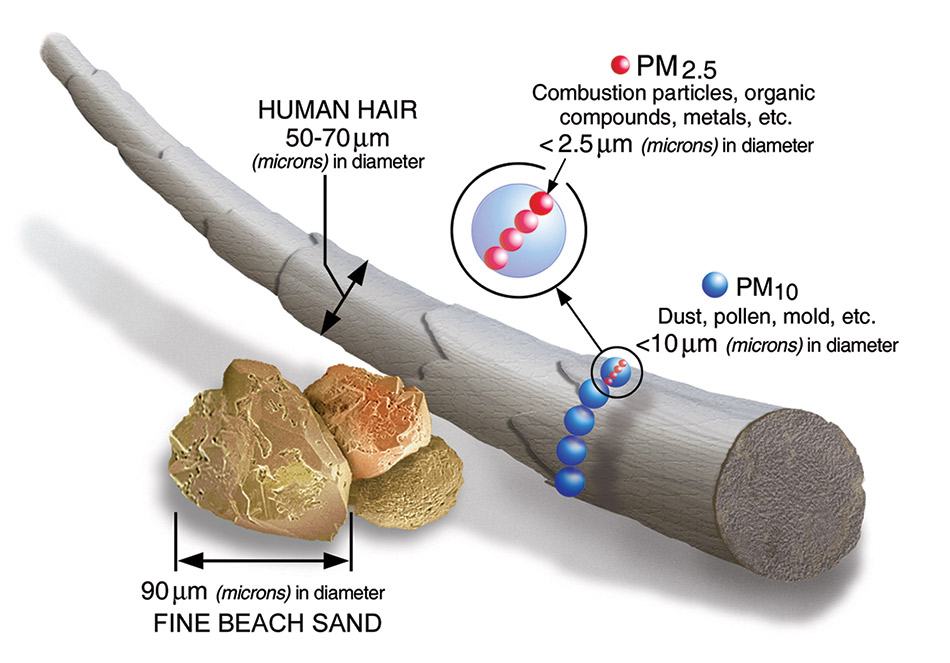
The relationship between air quality and health cannot be overstated, as poor air conditions are linked to various adverse health effects. Recognizing vulnerable populations and addressing their needs is essential for promoting public health in Vietnam.
6.1. Respiratory Diseases Linked to Poor Air Quality
Poor air quality has been associated with numerous respiratory diseases, including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and lung cancer. The inhalation of pollutants can irritate lung tissue and cause long-term health complications.
Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the effects of air pollution. Their developing or weakening immune systems make them more susceptible to respiratory problems, underscoring the need for focused health interventions in these groups.
6.2. Vulnerable Populations and Air Pollution
Certain populations in Vietnam face heightened risks due to their exposure to polluted air. Low-income communities often reside in areas with higher pollution levels, compounding existing health disparities.
Additionally, workers in industries associated with high emissions may encounter severe health risks without adequate safety measures. Ensuring that vulnerable populations receive proper education and resources to protect themselves is imperative in addressing the health implications of air quality.
7. Traditional Practices and Modern Solutions

Combating air quality challenges often requires a blend of traditional practices and modern technological solutions. Both approaches can work together to create a sustainable environment for future generations.
7.1. Indigenous Knowledge of Air Quality Management
Traditional practices rooted in indigenous knowledge provide valuable insights into managing air quality. Many communities across Vietnam possess a wealth of information regarding sustainable agricultural practices and natural resource management.
For example, traditional farming methods may include crop rotation and organic fertilizers, which contribute to improved soil health and reduced reliance on chemical inputs. Integrating these practices can enhance air quality while preserving the environment.
7.2. Technological Innovations for Cleaner Air
Advancements in technology present exciting opportunities for improving air quality in Vietnam. Clean energy initiatives, such as solar and wind power, hold the potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, thereby lowering emissions.
Innovative monitoring systems enable the collection of real-time data on air quality, empowering authorities and communities to respond effectively to pollution events. Furthermore, eco-friendly transportation solutions, such as electric vehicles and bike-sharing programs, offer practical alternatives to conventional modes of transport.
8. Future of Vietnamese Air: Challenges and Opportunities
Looking forward, addressing the challenges posed by air pollution while seizing opportunities for improvement remains paramount. Collaboration among governments, communities, and individuals will be essential for creating a sustainable future.
8.1. Sustainable Development Goals
Aligning air quality initiatives with sustainable development goals is vital for promoting environmental health in Vietnam. By prioritizing clean air as part of broader sustainability efforts, the country can enhance public health while fostering economic growth.
Investments in green infrastructure, such as parks and renewable energy, can create healthier urban environments that reduce pollution levels. Policymakers must identify actionable strategies that integrate air quality considerations into national and local development plans.
8.2. Community Involvement in Air Quality Improvement
Community engagement is a critical component of enhancing air quality in Vietnam. Encouraging local involvement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility toward the environment.
Educational programs can empower residents to take action, whether through supporting clean transportation options, participating in tree-planting initiatives, or advocating for stricter pollution controls. Collective efforts can lead to meaningful change, ensuring that cleaner air becomes a shared goal for all.
Xem thêm: Vietnam Airline Companies: The Gateway to Vietnam
9. Conclusion
The unique characteristics of Vietnamese air reflect a complex interplay of natural elements, climate variations, and human activities. By understanding the composition, pollution sources, health implications, and available solutions, we can better appreciate the importance of preserving air quality. With concerted efforts from the government, communities, and individuals, the future of Vietnamese air holds the promise of cleaner, healthier environments for generations to come.
OTravel Vietnam | Ready to Start Your Adventure in Vietnam
• Phone: (+84) 816 616 466 (WhatsApp/ Zalo/ Viber)
• Email: OTravelVietnam@gmail.com
• Website: www.otravel.vn
• Facebook: facebook.com/OTravelVietnam / facebook.com/OTravelcom
At OTravel Vietnam, we provide seamless travel solutions to help you explore the beauty of Vietnam. From personalized tours to unforgettable experiences, we ensure every journey is memorable. Contact us today and let your adventure begin!”







